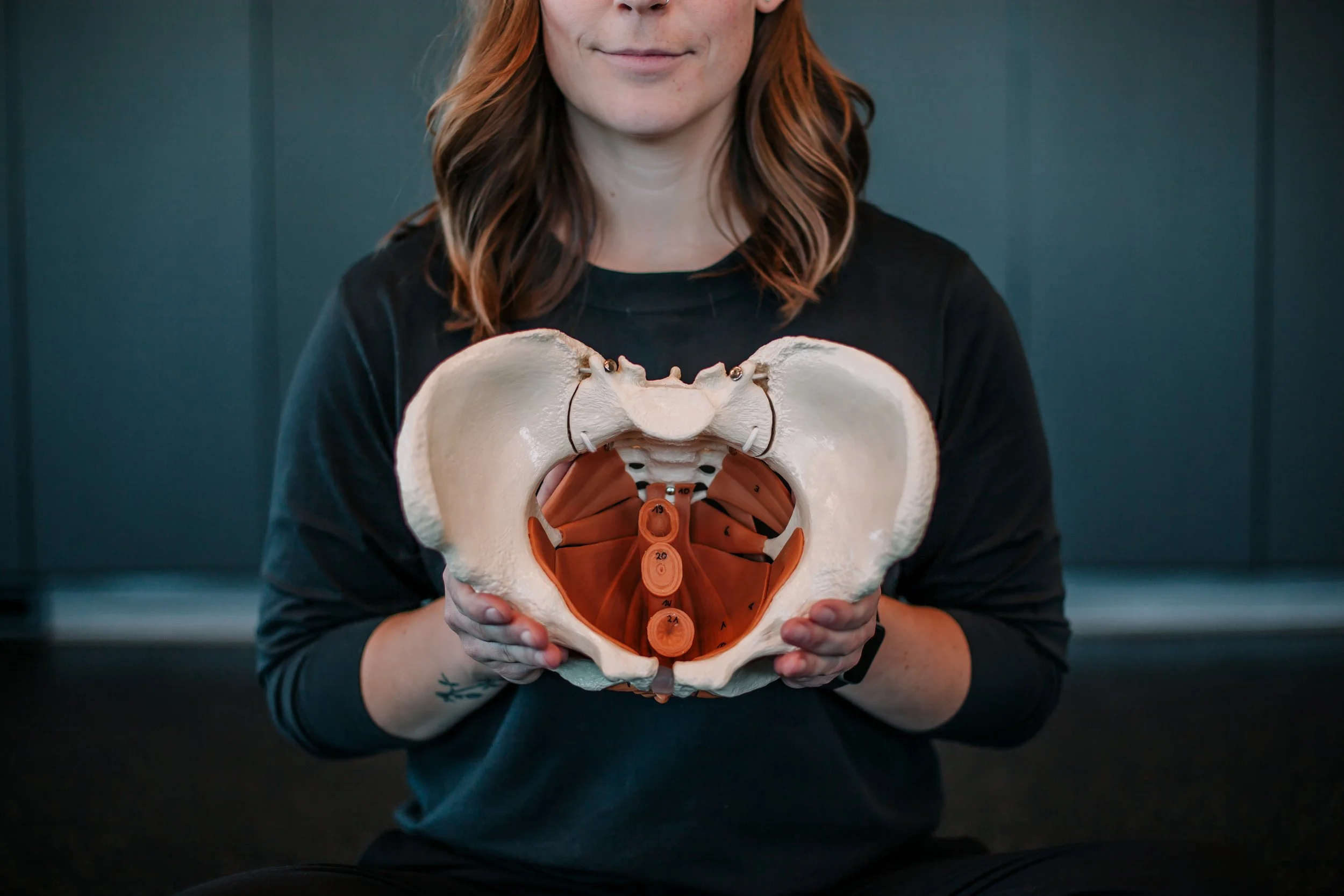
The pelvic floor is a vital yet often overlooked part of the body, playing crucial roles in various functions such as supporting pelvic organs, controlling bowel and bladder movements, and contributing to sexual function. Despite its importance, many people are unfamiliar with the anatomy and functions of the pelvic floor. In this blog post, we'll delve into the pelvic floor's anatomy and its roles in maintaining pelvic health.
Anatomy of the Pelvic Floor:
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and connective tissues that form a supportive hammock-like structure at the base of the pelvis. It consists of layers, each with its own unique function:
Superficial Layer: Contributes to sexual function and anchors the deeper muscles, and external anal sphincter
Intermediate Layer: The intermediate layer consists of the urogenital diaphragm, which supports the urethra and vagina in females and the urethra in males.
Deep Layer: The deepest layer of the pelvic floor includes the levator ani muscles, which provide structural support to the pelvic organs and help maintain continence.
Roles of the Pelvic Floor:
Supporting Pelvic Organs: One of the primary functions of the pelvic floor is to support the pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus (in females), and rectum. These organs rest on the pelvic floor muscles, which help prevent them from descending or prolapsing into the vaginal or rectal canal.
Controlling Bowel and Bladder Movements: The pelvic floor muscles play a crucial role in maintaining bowel and bladder continence. These muscles relax to allow for the passage of urine and stool and contract to prevent leakage or incontinence.
Stabilizing the Core: The pelvic floor is an integral part of the core musculature, working in conjunction with the deep abdominal muscles, back muscles, and diaphragm to provide stability and support to the spine and pelvis.
Contributing to Sexual Function: The pelvic floor muscles are involved in sexual function and pleasure for both men and women. In females, these muscles help support the uterus and vaginal canal, while in males, they play a role in erectile function and ejaculation.
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy and roles of the pelvic floor is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By acknowledging the significance of the pelvic floor in supporting pelvic organs, controlling bowel and bladder movements, stabilizing the core, and contributing to sexual function, individuals can appreciate the importance of pelvic floor health in their daily lives.